- Stud High Low Poker Rules Free
- Caribbean Stud Poker Rules
- Omaha Poker High Low Rules
- Hi Low Poker Rules
- Stud Poker Rules
- Five Card Stud Poker Rules
- Poker Rules
- Stud High Low Poker Rules For Sale
Omaha Hi/Lo Rules. Omaha Hold'em, 8 or better high-low split was in definite need of shortening, so poker players commonly refer to it as Omaha/8 or Omaha hi/lo. As with any other game of poker, the rules are mostly simple, but mastering the game requires a talented, relentless student. Two Plus Two Poker Forums Other Poker Strategy Stud: Stud Hi/Lo with a Declare rules question: Who wins the pot?? Straight flush for high, and a 7-low. Seven-card stud eights or better, also known as seven-card stud hi-low, is a split-pot game, played with two to eight players. As in regular seven-card stud, every player is dealt a total of seven.
Introduction
This has become one of the most popular forms of poker, both in formal play and in home poker where it is the basis of numerous variants. Each player is dealt a seven-card hand, some of the cards being face up, with several betting rounds during the deal. At the showdown players use any five of their seven cards to make the best poker hand. Seven-card stud works well as a high-low game, and there is also a low only form known as Razz.
This page assumes some familiarity with the general rules and terminology of poker. See the poker rules page for an introduction to these, and the poker betting and poker hand ranking pages for further details.
Players and Cards
A standard 52-pack is used and from 2 to 8 players can take part. The game is best for 5 to 7 players. When 8 play there is the problem that the cards may run out towards the end of the deal.
The Play
The sequence of events is as follows (as usual the cards are dealt clockwise one at a time):
- All players place an ante in the pot.
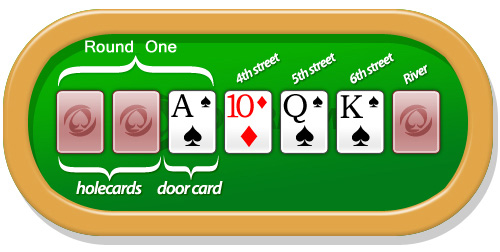
- Each player is dealt two cards face down and one face up. There is a betting round (third street).
- Each player is dealt a fourth card face up. There is a second betting round (fourth street).
- Each player is dealt a fifth card face up. There is a third betting round (fifth street).
- Each player is dealt a sixth card face up. There is a fourth betting round (sixth street).
- Each player is dealt one final card face down. There is a fifth betting round (seventh street).
- Surviving players have four face up and three face down cards. They show their cards and whoever can make the best five-card hand from their seven cards wins the pot.
The concealed cards - the first, second and seventh card dealt to each player - are sometimes known as 'hole' cards.
Order of Betting
Traditionally, each betting round is begun by the player with the best hand showing. For this purpose pairs, triplets, two pairs and quads count in their normal poker order - so for example with three cards showing 3-3-3 is higher than 7-7-8, which is higher than A-K-Q. Incomplete straights and flushes do not count. If there is a tie it is resolved by comparing the suits of the highest cards in the tied hands using the ranking order clubs (low), diamonds, hearts, spades (high).
Some play that in the first betting round (third street), the first player must place a compulsory bet, called the bring-in. In this case there may be no ante, though an ante is usually paid as well.
Some play that the first betting round starts with a compulsory (bring-in) bet by the player showing the lowest card. This is now the normal rule in formal games hosted by American casinos. The subsequent betting rounds from fourth street onwards are begun by the highest hand showing as usual.
Size of Bets
This is of course for the players to agree. Seven Card Stud is often played as a fixed limit game with the following arrangements.
- A small bet and a big bet size are determined - say for example $5 and $10.
- When there is a compulsory bring-in bet, the ante amount is generally much smaller than the small bet - say $0.50 in the example.
- The compulsory bring-in bet is normally less than the small bet but more than the ante - say $2 in the example.
- The player who opens the betting has the option to place a full small bet ($5) instead of just the compulsory minimum $2.
- If the opener just places the minimum bring-in, subsequent players have the option to complete the bet to a small bet ($5), to call the bring-in ($2) or to fold. Only if someone completes the bet are later players allowed to raise. If the opener chooses to begin with a full bet ($5), subsequent players can raise.
- In the first betting round (third street) no big bets are allowed.
- If there is no compulsory bet in the first betting round, then a larger ante should be used, and only full small bets are allowed in the first betting round.
- Only one bet and a maximum of three raises are allowed in any betting round, if there were more than two active players at the start of the betting round. A bring-in of less than a small bet does not count as a bet for this purpose - after it is completed there can be three raises.
- From fourth street onward, big bets ($10) are allowed if any player has a pair (or better) showing. In this case anyone can place a big bet or raise, even if they do not themselves have a pair.
- Note that if the rule is played that each raise must be at least as large as the last bet or raise, then after a player places a big bet, only big raises are allowed in that round. However, many home poker games do not have this rule, in which case a player may respond to a big bet with a small raise, thereby 'using up' one of the three raises and limiting the potential size of the pot.
- Some play that from fifth street onwards, only big bets are allowed. This is the normal rule in casino hosted games, but not in home poker games.
Running Out of Cards
If there are eight players and after sixth street no one has folded, there will not be enough cards to deal everyone a seventh card. In this case a single 'community' card is dealt face up to the table and this counts as everyone's seventh card. Everyone then effectively has five cards showing, including the community card, and seventh street betting is begun by the player for whom this makes the highest poker hand - straights and flushes not count. Ties are resolved by the suit of the highest card as usual.
In formal games it is usual for the dealer to 'burn' one card - placing the top card of the deck face down under the pot - at each stage of the deal. In this case the card can run out even with only seven players. If the dealer determines that there are not enough cards to complete the deal, the burned cards are retrieved from under the pot and shuffled with the remains of the deck, and if possible a card is then dealt to each player.
Note that in no case are cards discarded by a player who has folded returned to the deck to be dealt. These cards are dead.
Seven Card Stud High-Low
The deal and betting are mostly the same as in ordinary seven card stud. Some play that in high-low games, a pair showing does not give players the option of a big bet or raise.
At the showdown, each player selects five cards to make a high hand and five possibly different cards to make a low hand. The pot is split equally between the highest and lowest hands, the odd chip going to the high hand if the amount cannot be divided exactly by two. Any of the possible low hand ranking methods can be used - see low hand ranking on the poker hand ranking page.
Since different selections of cards can be used for the high and low hands, it is entirely possible for one player to win both halves of the pot.
In formal games, the rule is that 'the cards speak for themselves'. That is - at the showdown each player is entitled to compete with the highest and lowest hand that can be made from his or her seven cards, even if the player does not correctly identify the best selections of five cards.
Eight or Better
In formal games there is often a qualification rule that a low hand cannot contain any card higher than an 8. In this case the ace-to-five system of low hand ranking is used. This variant is called Seven Card Stud Hi-Lo Eight or Better, often abbreviated to Seven-Stud/8. If none of the players has a qualifying low hand at the showdown, the high hand wins the whole pot.
With Declare
In home games, Seven Card Stud High-Low is often played with declaration. After the seventh street betting round each player has to declare either 'high', 'low' or 'both'. This can be done either in sequence around the table or simultaneously. In the simultaneous method each player holds out a closed fist containing one chip for 'high', no chips for 'low' or two chips for 'both', and when all are ready, everyone reveals their choice.
In the showdown, if no one declared 'both', the highest hand among the players who have declared 'high' shares the pot with the lowest of the players who have declared 'low'. If all declare 'high' or all declare 'low', the winner takes the whole pot. A player who declared 'both' has to have the highest hand or all the 'high' and 'both' players and the lowest hand of all the 'both' and 'low' players to win the whole pot. A 'both' player who loses or ties either high or low cannot win any part of the pot.
See the sections on declaration methods and the showdown in split pot games on the poker betting page for further details and variations.
Razz
Razz is seven card stud played for low only, using ace-to-five ranking (see hand ranking in low poker). In the first betting round the compulsory bring-in bet is made by the owner of the highest card showing. In subsequent rounds, from fourth street onwards, the lowest hand showing bets first. Ace is low and king high throughout, and as usual the suit of the highest card is used to break ties, so if on fourth street two players tie for lowest with 6-2 and 6-2 the second hand will start the betting, because the six of clubs is lower than the diamond.
In fixed limit games the limits double at fifth street: on third and fourth street only small bets are allowed, and from fifth street onwards only big bets. Pairs showing have no effect on the size of bets.
The RAZZ page of the Play Lowball Poker site has further information on the history and variants of this game.
London Lowball
London Lowball is seven card stud played for low only, using ace-to-six ranking (see hand ranking in low poker).
Normally a pot limit betting structure is used (see betting limits).
Seven Card Stud with Wild Cards
In home poker, seven card stud is often played with wild cards, which of course increases the frequency of the higher hand types. In the simplest case the wild cards can be all cards of a certain rank, as agreed by the players or specified by the dealer in a dealer's choice game - for example seven card stud, deuces wild. The game with wild cards can of course also be played high-low or low only.
There are also some more elaborate seven-card stud variants in which the wild cards are determined by the players' cards in the course of the deal.
Low Hole
This game, also known as Late Show, is seven card stud in which each player's lowest concealed card is wild for that player only. That means for example that if your first three cards are 9-4 face down and 3 face up, all your fours will be wild unless your seventh card, which will also be face down, is a 3 or a 2, making that rank wild instead.
Low Hole is normally played as a high game, but can also be played low or high-low. In the case of high-low, if you use ace-to-six or ace-to-five ranking of low hands, then an ace in the hole will make aces wild for the purpose of low hands but not for high hands.
English Stud
Six players are the maximum for this variant, in which players can improve their hands by substituting cards.
Deal, play and betting are the same as in seven-card stud up to the point where each player has five cards (two down and three up). After the subsequent betting round and before the sixth card is dealt, each player in turn, starting with the player to dealer's left, has the option to exchange any one card. The player may either discard a down card and be dealt a new down card or discard an up card and be dealt a new up card, or choose to stand pat and not exchange any card. Then a sixth card is dealt to each player face up, there is a betting round and another round of exchanging. There is a final betting round followed by a showdown.
Variations
If there are five or fewer players, a seventh face-down card can be dealt, as in seven-card stud.
Some set a price for exchanging, which may be equal to the minimum bet at that point. In this case, anyone who exchanges must pay that amount to the pot. This does not count as a bet and does not have to be matched by the other players.
Aces, Straights and Flushes
Brian Johnson describes this game, in which each player is dealt six cards and there is a joker in the centre of the table that acts as everyone's seventh card. The joker is not fully wild, but functions rather like the 'bug' in 5-card draw. It can represent an ace, or a card needed to complete a player's straight or flush, but cannot be used to form a set of equal cards other than aces. Deal and betting are the same as in seven-card stud up to the point where each player has five cards (two down and three up). After the ensuing betting round each player gets one last face down card and there is a final betting round.
Stud High Low Poker Rules Free
Stud poker is any of a number of pokervariants in which each player receives a mix of face-down and face-up cards dealt in multiple betting rounds. Stud games are also typically non-positional games, meaning that the player who bets first on each round may change from round to round (it is usually the player whose face-up cards make the best hand for the game being played). The cards dealt face down to each individual player are called hole cards, which gave rise to the common English expression ace in the hole for any hidden advantage.
- 3Specific variants
Caribbean Stud Poker Rules
History[edit]
Stud poker variants using four cards were popular as of the American Revolutionary War. Five-card stud first appeared during the American Civil War when the game was much played among soldiers on both sides, and became very popular. Later, seven-card stud became more common, both in casinos and in home games.[1] These two games form the basis of most modern stud poker variations.
Play[edit]
The number of betting rounds in a game influences how well the game plays with different betting structures. Games with four or fewer betting rounds, such as five-card stud and Mississippi stud, play well with any structure, and are especially well suited to no limit and pot limit play. Games with more betting rounds are more suited to fixed limit or spread limit. It is common (and recommended) for later betting rounds to have higher limits than earlier ones. For example, a '$5/$10 Seven-card Stud' game in a Nevada casino allows $5 bets for the first two rounds and $10 bets for subsequent rounds. Also common is to make the final round even higher: a '$5/$10/$20' game would allow $20 bets on the last round only. Another common rule is to allow the larger bet on the second round if there is an 'open pair' (that is, at least one player's upcards make a pair). Some casinos (typically in California) use the smaller limit on the first three rounds rather than just the first two.
It is a common convention in stud poker to name the betting rounds after the number of cards each player holds when that betting round begins. So the bet that occurs when each player has three cards is called 'third card' or 'third street', while the bet that occurs when each player has five cards is 'fifth street'. The final round, regardless of the number of betting rounds, is commonly called the 'river' or simply the 'end'.
Specific variants[edit]
As mentioned above, seven-card stud is probably the most common form of the game, with most other games being variants of that, although five-card stud is also a basic pattern upon which many variations are built.
Omaha Poker High Low Rules
Six-card stud[edit]
Six-card stud is usually played as identical to seven-card stud, except that the last face-up round is removed (thus it is two down, three up, one down). It can also be played as 1-4-1, where the first betting round occurs after only two cards are dealt (one down and one up). This latter form more closely resembles five-card stud with an extra downcard.
Razz[edit]
Razz is a variant where the lowest hand wins the pot instead of the highest. Versions differ in the rules for treating straights and flushes as high or low. London Lowball is a popular version that counts straights against the player.
High-low stud[edit]
Hi Low Poker Rules

Stud Poker Rules
High-low stud is played using high-low split betting, where the pot is split between the player with the highest hand and the player with the lowest hand. In the most common form, known as 'eight-or-better' or 'stud eight', an 8-high hand or lower is required to win low. If there is no qualifying low hand, high hand takes the entire pot.
Five Card Stud Poker Rules
Another form of high-low split stud is played under the same rules as stud eight, but there is no qualifier required for the low half of the pot. Often referred to as Q, it is much less common than stud eight, and is generally played at higher limits.
Mexican stud[edit]
Various forms of roll your ownfive-card stud, often with a stripped deck and wild cards, are called Mexican stud, Mexican poker, or stud loco. One such variant played by the Casino San Pablo in northern California has these rules: 8s, 9s, and 10s are stripped from the deck, and a single joker is added (the deck therefore contains 41 cards). The 7-spot and the J become consecutive, so that 5-6-7-J-Q is a straight. A flush beats a full house (with fewer cards of each suit, they are harder to get). The joker plays as a bug if it is face up, and fully wild if it is face down. The game is played as five-card stud choose-before roll your own. It is usually played with a very high ante, and the high card on the first round pays the bring-in.
Poker Rules

The game of Shifting sands is Mexican stud in which each player's hole card (and all others of that rank) are wild for that player only.
Caribbean stud[edit]
Caribbean Stud Poker is a casino game that has been developed using the poker hands and general rules of 5 card stud poker. The game combines poker elements and standard table game elements in that each player dealt into the hand is playing against the dealer. Originally invented by gambling author David Sklansky using the name Casino Holdem with some slight rule variations,[citation needed] the game was first introduced at the Grand Holiday Casino and eventually all the remaining hotels in Aruba in the 1980s.
Miscellaneous[edit]
- Five-card stud played high-low split with an added twist round is called Option alley or five-card option.
- The game Scandinavian stud or Sökö is five-card stud with two new hand values added: Four-card flush and four-card straight. Hand ranking is therefore: High card, one pair, four-card straight, four-card flush, two pair and then on as usual. A four-card straightflush is not a hand in itself, it's merely counts as a four-card flush.
- The term English stud is used ambiguously to refer to several games, including six-card stud played 1-4-1 with a twist (also called six-card option), London lowball, and a seven-card stud game where both sixth street and seventh street are twist rounds.
- In the game of seven-card flip, each player is dealt four cards face down, and chooses two of them to turn up. All cards are turned up simultaneously after everyone has chosen. As this point, the game proceeds as if it were standard seven-card stud starting on fourth street.
- Kentrel, or '48', is a seven-card stud variation which starts with each player being dealt four downcards. Each player must then discard one, choose one of the remaining three to turn face up (leaving two down and one up as normal), and then proceed as with eight-or-better high-low stud.
- The game of Show Hand, which is not commonly played but made famous by Hong Kong gambling films, is a twist in 5 card stud. Players with the highest face up cards decide whether to check the round or raise; or, if the player with the highest face up card or hand checks, it will proceed to the next street. However, the last round of betting after the river is dealt is unlimited. In Show hand poker the last card is dealt face down. Players now choose from 1 of the 2 face down cards to reveal to other players. This variant is usually played with a set time-limit and bet limit to prevent players from taking advantage of checks and not betting to prolong the game.
- The game of Chicago is seven-card stud in which the high hand splits the pot with the player who has the highest-ranking spade 'in the hole' (among his downcards). There is also Little Chicago (also called Southside), in which the lowest ranking spade in the hole splits the pot; players who play Little Chicago call the high spade variant Big Chicago. This also known as Chicago high by night and Chicago low by night. In Chicago by night the Deuces and One-eyed jacks are usually called as wild cards.
- The Bitch is a variant on Chicago above, played with a combination of up and down cards, usually two down, four up, and one down. The twist is that the Queen of Spades is designated as the highest ranking Spade, followed by the Ace, King, Jack, and so on. Also, if the Queen of Spades is ever dealt as an upcard to any player, all players turn in their cards, re-ante, and replay the game. This can lead to quickly increasing pots, especially if the re-ante amount is increased on each iteration. The high hand splits the pot with the high spade.
- Several different games played only in low-stakes home games are called Baseball, and generally involve many wild cards (often 3s and 9s), paying the pot for wild cards, being dealt an extra upcard upon receiving a 4, and many other ad hoc rules (for example, the appearance of the queen of spades is called a 'rainout' and ends the hand, or that either red 7 dealt face-up is a rainout, but if one player has both red 7s in the hole, that outranks everything, even a 5 of a kind). These same rules can be applied to no peek, in which case the game is called 'night baseball'. See main article: Baseball Poker.
- Cowpie poker is played as seven-card stud until after the seventh-street bet. All remaining players then split their hands into a five-card hand and a two-card hand. The five-card hand must outrank the two-card hand, and the latter must contain at least one downcard. After the split there is one more betting round and showdown. Upon showdown, the highest five-card hand and the highest two-card hand split the pot. The name of the game is a pun on Pai Gow.
- Number Nine is a variant of seven-card stud in which 9s are wild, and any two number cards that add up to 9 may make one wild card, at the player's option. Aces count as 1 for wild card purposes. The player is not obliged to make any wild cards, and can play cards that could make 9s at face value or as wild cards, at his option. Cards used to make wild cards may not figure in the resulting hand twice. The player cannot add three or more cards. Sometimes, 9s themselves are not wild, and wild cards can be made only by addition.
- Dr Pepper is a stud variant where 10's, 2's, and 4's are wild (the name comes from one of the original Dr Pepper advertisements of the 1920s: 'Drink a Bite to Eat at 10, 2, and 4 o'clock').
- Draft (or 'socialist poker') is usually a variant of seven-card stud in which the second and subsequent upcard rounds are dealt this way: for each player remaining, one upcard is dealt to the center of the table (not to any specific player). The player with the worst showing hand gets to choose which of them he will take for his next upcard, then the player with the second-worst showing hand chooses his upcard from those left, and so on, until the player who previously had the best showing hand takes the remaining card. Then betting occurs as normal. In seven-card stud, this makes for three 'draft' rounds (the first three cards are dealt normally, as is the final downcard).
- Auction is a similar variation in which each upcard round (or possibly just those after the first) begins with an 'auction' phase. Instead of dealing each player one upcard, the first card is dealt to the center and all players bid on it; the player who bids the highest amount places that amount into the pot, and then has the right to either keep the auction card as his own upcard, or designate another player who is required to take it as his. After the first card is auctioned off and placed, the remaining players are dealt a random upcard as usual, and betting proceeds as usual. This variation is commonly played as high-low split, so it is common for a player to 'purchase' a high card to force it upon an opponent seeking low, for example.
- Telesina is a stud variant which is played with a stripped 'French' deck. The play follows most five card stud games except that after the fourth betting round a 6th community card called the vela card is placed in the center of the table. The vela card may be used by all players to improve their hand after which another round of betting occurs. The standard hand ranking applies with the slight difference in that a flush beats a full house because it is easier to get a full house than a flush. This is because instead of 13 cards per suit there are only 8 having the cards from 2-6 removed.